 ARIZONA SWORDS
ARIZONA SWORDS 
 ARIZONA SWORDS
ARIZONA SWORDS 
Enfields-Revolvers-Muskets
CLICK BELOW BUTTONS TO SEE AVAILABLE ITEMS
Beware of fake and misrepresented edge weapons.
Click above to see examples of known fakes!
***********************************************************************************************************
CLICK IMAGES TO SEE MORE PHOTOS
******************************************************************************************************************************
C&BL01: CONFEDERATE GEORGIA – COOK & BROTHER RIFLE/CARBINE LOCK: This is an original and complete Confederate Georgia made Cook & Brother rifle/carbine lock. It is 100 % complete and properly functions. The lock is marked with the Confederate flag, COOK & BROTHER, ATHENS G, 1863, and serial number 3585. The screws both have matching assemble marks \ III, which match those of the main spring, and the front plate has a been notched to accept an Enfield barrel bolster. The entire front has an even patina, as does the internal parts. Shipping & Insurance included. $2500.00
*****************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
RROD01. SERIAL NUMBERED - CONFEDERATE ENFIELD RIFLE RAM-ROD: This is a serial number ram-rod for a Confederate Enfield Rifle. It is serial number 6301 and is 38 3/4 inches long. This number places it in the range of the 500 guns produced by James Kerr. Kerr Enfield rifles represent slightly less than 2% of the total delivered and to date only 6 of the 500 P-1853s delivered by James Kerr are known to still exist. The Enfield rifle with this number is one of those surviving examples, but the whereabouts is unknown. It has the same serial number and is “K” marked forward of the butt plate with a JS-Anchor worn off. If you have this rifle let me know. Shipping & Insurance is included. $1900.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F362. CONFEDERATE “K” & "JS ANCHOR" MARKED - NUMBERED P-1853 ENFIELD: During the early days of the war, Confederate purchasing agents secured contracts for the British P-1853 Enfield Rifle Musket, and according to Confederate Chief of Ordnance, Josiah Gorgas’s, some 70,980 Long Enfield Rifles were purchased from the beginning of the war through the end of 1862. These numbers only account for Confederate central government purchases, and not those purchased by states or by profiteers. The majority were purchased from S. Isaac, Campbell & Company or Sinclair, Hamilton & Company. They had several contracts with the Confederacy to deliver P-1853 Enfield Rifle Muskets, with the typical contract terms requiring 30,000 stands of arms to be delivered over a six-month period. Sinclair, Hamilton & Company appears to have received at least five of these Confederate central government contracts for P-1853 Enfield Rifle Muskets. The second of these contracts for 30,000 P-1853 “Long Enfields’ is the one represented by the guns with the JS / (ANCHOR) inspection mark, along with the engraved butt plate tang inventory control numbers. These numbers ran from 1-10,000 in three series. The first series had no suffix after the number, while the second series of 10,000 had an “A” suffix under the inventory number and the third series of 10,000 had a “B” suffix. Sinclair, Hamilton & Company acquired their arms through “Five Furnishers.” The London furnishers were the longtime gunmakers EP Bond and Parker, Field & Co, with James Kerr receiving a tiny portion of the contract (only 500 guns). The balance was delivered by the Birmingham firms CW James and W.C. Scott & Son. The furnishers often marked the guns delivered with a large single letter on the upper comb of the stock: B for Bond, F for Parker, Field & Co, J for James, K for Kerr and S for Scott & Son. An October 31, 1861 dated letter from Sinclair, Hamilton & Co. notes that the contract was divided between the furnishers as follows:
CW James: 10,000
Scott & Sons: 8,000 guns
E.P. Bond: 6,000 guns
Parker, Field & Co: 5,500 guns
James Kerr:500 guns
Kerr marked Enfield rifles represent slightly less than 2% of the total delivered. To date only 6 of the 500 P-1853s delivered by James Kerr under this contract have been noted. Of the 6 known specimens, 2 are marked CARR / LONDON on the lock, three have blank unmarked locks, and one is marked 1861 / TOWER. Two of the guns are the obsolete “Type II” P-1853 Enfield rifle musket with solid barrel bands retained by springs, and the other are the typical “Type III” Enfield pattern arms. Due to the very small delivery total and extremely low survival rate, James Kerr furnished, P-1853 Enfields are extremely rare and the hardest examples to locate! It is often missing from even the most advanced collections of Confederate imported Enfields. This gun is in attic condition and is complete with the original numbered ram-rod, barrel bands and sling swivels, but missing the rear site blade. The butt plate and ram-rod are serial number 5945 and the letter “K” is stamped in the stock forward of the butt plate tang. The JS Anchor stamp is very faint and not visible with the naked eye; however a ghost image of the mark is barely visible with magnification. Shipping & Insurance included. Shipping & Insurance included. $9000.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
“Z”
F379. RARE! - CONFEDERATE CAPTURED, CLEANED & REPAIRED NEW MODEL SHARPS, UNION RECAPTURED AND POST WAR CONVERTED TO .50-70 CARBINE: This is an extremely rare Civil War & Post War Sharps Carbine. It originally started as a New Model Sharps and was issued early in 1865 to union troops, was Confederate captured and went through the Clean & Repaired process, butthen Union recaptured and later converted to .50 – 70 in 1868 for Indian War use. The serial number on this gun is C19440. C19358 went to the 15th New York Cavalry and C19543 went to the 8th New York Cavalry, so it is likely this gun when to one of those two units, which where both fighting in Virginia during the advance on Richmond. This Sharps Carbine went through the Confederate C&R (clean, repair) process and has the inspection mark “Z” on the underside to the rear of the trigger tang. This mark is associated with Captain Louis Zimmer, who was involved with Confederate clean and repair operations at Richmond. It is unknown exactly what work was done on the gun during the C & R process, and I doubt the gun was ever reissued to Confederate troops as Richmond fell. The gun is in amazing condition. The barrel is marked New Model 1863 to the rear of the site with faint HARTFORD CT mark to the front. The SHARP maker mark is on the front of the lock with the correct marks on the opposite side. The barrel retains 98% + original finish and has a bright 6-grove bore, and there is a good amount of case-coloring on the gun. The stock is in near-mint condition and there is the post-war cartouche that was applied when the gun was converted to .50-70. There is a small chip on the forearm of the stock, but otherwise also near-mint. From February 1868 to October 1869, approximately 32,190 carbines were switched over to the .50-70 cartridge. The carbines were immediately sent to the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 6th, 7th, 8th, 9th and 10th Cavalry Regiments in the West. This is an amazing example of a Sharps Carbine which saw action in Virginia during the Civil War, was Confederate captured and Union recaptured, and later converted to .50-70 for Indian War Service. Shipping & Insurance included. $7900.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
F395. CONFEDERATE ALTERED - HARPERS FERRY 1842 MUSKET - 1845 DATED: This 1842 Harpers Ferry musket is Confederate altered to the size of a 2-band rifle, and once had a Confederate blade site. It is in attic-found condition and has not been cleaned and is all original! The stock is rough with a few splits in the stock near the left side of the barrel, but the wood is strong and not loose. The lock properly functions in both half & full cock position and is dated the same as the barrel;1845. The ramrod is originally for an 1860 Springfield rifle, but was shorten and treaded at its bottom, not just cut down. On the top of the barrel, you can see two groves for a Confederate blade site, which is long gone. There is also is saddle wear on the underside forward of the trigger guard. Shipping & Insurance is included. $895.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F399. “G” MARKED, SERIAL NUMBER BUTT PLATE, JS-ANCHOR MARKED PATTERN-1853 ENFIELD RIFLE: This is a Georgia “G” marked, serial numbered butt plate, JS-Anchor marked 1853 Enfield rifle, which went through the Clean & Repair process most likely at a Macon arsenal. Where as the C & R process in Richmond had an inspection system with inspector marks, Macon did not, but the work was similar. Since this gun was originally purchased by the state of Georgia, it can be assumed it was also repaired in Georgia.
The stock would have been refinished, which accounts for the “G” marks being faint. The original barrel most likely sustained battle damage and was replaced with a PRITCHER barrel as is evident by the vice clamp marks. There is no rear site, but a site notch was cut into the rear barrel band. The butt plate serial number is 1449, and the JS Anchor is to the rear of the trigger tang and is readable. The lock is correctly dated 1861.
The serial number places this gun within the Gladiator range and Gladiator range serial number butt plate Enfield are rare. Even more unique is one that was Macon arsenal repaired. Shipping & Insurance included. $6500.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
F427.ENGLISH - BRITISH PATTERN 1855 ROYAL ENGINEER’S CARBINE - ROYAL SAPPERS & MINERS CARBINE, WITH LANCASTER’S OVAL BORE: In January of 1852, the British Board of Ordnance began taking the first tentative steps towards designing what would eventually become the Pattern 1853 Enfield Rifle Musket. It was the knowledge that a smaller bore rifle musket was necessary to stay competitive with the armies of Europe. The submissions by the various makers were all different calibers and with different patterns of rifling and each used a bullet of their own design, with only constant that the bullet weight was to be about one ounce, a weight considered the minimum for an effective infantry musket. Lancaster’s submission was his “oval bore” design. This was a mechanical rifling system that from all appearances was a smoothbore design. However, the bore was very slightly oval in cross-section with a minor axis of .543” and a major axis of .557” at the breech, which was slightly reduced to .540” and .55” at the muzzle. The bore itself twisted along the length of the barrel, creating mechanical rifling similar to the systems that would be subsequently patented by Sir Joseph Whitworth and Westley Richards. The pitch of the rifling also increased along the length of the bore, in other words the rifling spun slower at the breech and more quickly at the muzzle. The oval bore rifling performed very well in the trials, as did the five-groove design of Wilkinson and the 3-groove design submitted by Enfield. These experimentations resulted in what would become the basic design specifications for the Pattern 1853 Enfield Rifle musket: a 39” barrel secured by three-barrel bands, with a .577” bore, rifled with 3-grooves with a 1:78 rate of twist, weighing in at slightly more than 9 pounds including the socket bayonet, which would incorporate a locking ring. It was further specified that the lock would include a “swivel” (stirrup) so that the mainspring did not bear directly upon the tumbler as it did in earlier designs. The specification regarding a rear sight remained somewhat open to discussion, as several designs had been submitted, several of which were quite good. Interestingly the rifling pattern was not completely established either, for although the initial specifications called for the three-groove bore of Enfield design, the performance of the Lancaster and Wilkinson pattern rifling left significant doubt in the minds of the Small Arms Committee as to whether the correct decision had been taken as to the style of rifling to be use. A bullet design, which was a collaboration of William Pritchett and William Metford, was adopted for use in the nominally .577 bores of the guns. In January of 1853, an order for 1,000 of these newly specified rifle muskets, 500 with one pattern or rear sight and 500 with another, was placed, in order to begin real field trials of the weapon. In the end the sight designed by Charles Lancaster became the rear sight that we are familiar with on the Pattern 1853 Enfield today. The result of the committee’s lack of confidence that they had “chosen wisely” regarding the rifling system was readily apparent in early 1853, when Wilkinson and Lancaster were both asked to submit Pattern 1853 Enfield Rifle Muskets that conformed exactly to the pattern as was newly adopted, with the only exception being the rifling of the bores, which were to be of the two makers’ patent designs. In June of 1853, the trials of the three rifling systems began and the Lancaster oval bore shot better than either of its competitors. Initially, Lancaster asked to have his guns fired with his own cartridges that used specially sifted powder. However, it was soon discovered that the standard British military service load with standard service powder and the 530 grain Metford-Pritchett bullet shot better in the Lancaster gun than his own specially designed cartridge! Wilkinson insisted on using his own proprietary cartridge as well and did not acquiesce to the use of the standard service load during testing. The result of testing the three systems at 500 yards, aimed at a 6’ foot target resulted in the Lancaster rifling system placing all shots in a 4’ group, while the Enfield rifling could only keep 75% of the shots on target at that distance. The Wilkinson system fared far worse, failing to reliably keep shots on the 6’ target at 200 yards! The results of the testing were so promising that an additional 20 oval bore P1853s were ordered from Lancaster for further evaluation by the Committee on Small Arms. In addition, it was decided to issue the available 3-groove P1853s very sparingly, in the event that Lancaster’s system was eventually adopted over the Enfield 3-groove bore. To further indicate that the decision was not yet set in stone, it was ordered that all P1853s in the production pipeline (some 20,000 contract arms) be made smoothbore, pending the final decision regarding the rifling pattern. The additional testing in August of 1853, shooting at distances of up to 800 yards, again showed the superior accuracy of the Lancaster design. However, two issues had raised concerns among the nay-sayers who supported the Enfield pattern rifling. The first was that the increasing spiral of the bore was complicated and difficult to produce, which would make it harder for the various arms contractors (as well as R.S.A.F.) to manufacture the Lancaster patent barrels. The second concern was that the relief at the breech, being slightly larger than the muzzle, could allow a loaded bullet to move forward when the arm was in service, leaving an air gap between the bullet and the powder charge. It was feared that this gap might create an unsafe situation resulting in increased pressures and a burst breech when the gun was fired. Lancaster subsequently performed tests with bullets that were not fully seated, which proved that this fear was unwarranted. However unfounded, the concern would affect further testing of the Lancaster system and in some ways conspired to help it fail.
In late August, five trial P1853 Enfields were set up at Enfield with Enfield made, Lancaster patent barrels. The barrels had a minor axis of .577” and a major axis of .587” and has the standard 1:78” rifling pitch. The barrels did not have the breech relief of the Lancaster made barrels, nor did they use progressive twist rifling, so the rate of twist remained constant through the length of the bore. These five rifles were tested against Lancaster’s submissions and were found to be sorely lacking, with the Lancaster produced rifles placing 99 of 100 rounds in a reasonable group on a 300-yard target, and the Enfield produced oval bores missing the target entirely 68 times at the same distance! Amazingly, this additional confirmation only resulted in additional testing, with the Board of Ordnance’s decision-making process moving with all the speed of a receding polar ice cap! This fourth series of tests of the Lancaster system in 1853 again proved that the oval bore rifling was superior not only to the conventional 3-groove rifling employed at Enfield, but also to the Enfield made version of the oval bore. In these tests, the Enfield “oval bore” showed a tendency to “strip” after a significant amount of firing, what a modern shooter would refer to as the bore being “shot out”, with the rifling being worn beyond the point of serving its purpose. While the Lancaster made rifles did not show this tendency, it was implied that since this defect existed in the Enfield made arms, that “production quality” oval bore rifles, not produced with the same precision as Lancaster’s trial rifles, would suffer the same fate. Thus, a fifth set of tests were performed in November 1853, this time eliminating the Enfield made oval bores and once again putting the Lancaster oval bore in a head-to-head competition with the 3-groove Enfield. This last series of tests for 1853 showed that even Lancaster’s well-made guns, after a significant amount of firing, began to “strip” as the Enfield made versions had. The report noted that no visible (or even measurable) deterioration was noted, but that after repeated firing the accuracy of the guns gradually eroded. It appears that the Small Arms Committee was performing the tests with the same five trials rifles that had been supplied that summer, and it was likely at this point that thousands of rounds had been fired through the guns. Amazingly, this report resulted in a new series of tests in early 1854. This sixth test required more than 1,000 rounds to be fired from a single Lancaster oval bore rifle musket versus a standard Enfield P1853. As had been discovered in the final testing at the end of the previous year, the Lancaster system began to “strip” and the accuracy degraded over time. The reason for the failure could not be discovered, and as the oval bore system was so much more accurate than the 3-groove system when the bore was new, the supporters of Lancaster’s design lobbied for another test (the seventh) in February of 1854, with the results being the same. At this point, it appears that serious pursuit of the Lancaster rifling system by the Small Arms Committee was abandoned. However, only a year later, Lancaster’s design was adopted for limited production and issue to the Royal Engineer Corps, as the Pattern 1855 Royal Engineer’s Carbine, or more commonly as the Royal Sappers & Miners Carbine, with Lancaster’s Oval Bore. So, as we can see the oval bore concept was far from dead and still had several supporters with the small arms and ordnance communities. The Pattern 1855 Royal Engineer’s Carbine looks very much like the Pattern 1856 Enfield “Short Rifle” at first glance. The brass mounted rifle had a 31.5” round barrel, secured by two clamping barrel bands and was nominally 48” in overall length. A bayonet lug to accept a saber bayonet was mounted to the barrel, near the muzzle. Like most variants of the shorter “Enfield” pattern long arms, the lower swivel was mounted in the toe of the stock and the upper swivel was attached to the upper band. While the 1.5” difference in length between the barrels of the Royal Engineers “Sappers & Miners” carbine and the Pattern 1856 short rifle is not immediately noticeable, the mounting of the rear sight “backwards” from the conventional direction on the Lancaster guns is a quick identifying feature. Due to Lancaster’s control of the patent, he managed to be the only contractor to produce the military contract Royal Engineer’s Carbines from their adoption through November of 1858. After that time, contracts were let to the various Birmingham and London makers who could produce the gun. However, the guns were never acquired in large numbers as their issue was to a very specific and small branch of the British military. Despite the limited production for British military use, the outstanding accuracy of the Lancaster design found favor with the British “Volunteer” movement.
Offered here is a GOOD condition example of a scarce Pattern 1855 Royal Engineer’s Carbine. The gun is clearly marked on the lock, in two engraved lines: C. LANCASTER’S / PATENT. The barrel is further engraved: 151 NEW BOND ST LONDON. The barrel measures 31.75”; the top of the barrel is stamped with the usual London commercial view, proof and definitive proof marks, as well as the gauge mark 25, indicating a nominally .577 bore. The “carbine” has the correct pattern leaf rear sight that is mounted in reverse with the 1000-yard graduations on the bottom of the leaf, so they are seen by the shooter when it is lifted. The original front sight, an improved version of the standard military “block and blade” sight, is present near the muzzle. The saber bayonet lug is of the correct Pattern 1856 “Type I” pattern with a .75” key forward of the main lug. The exposed iron surface shows light pitting, but it is under a deep brown attractive patina. The lock has a slightly mottled plum brown and gray patina, with double boarder line engraving that remains clear and sharp, as does the engraved Lancaster information. The lock is mechanically excellent and functions perfectly. As noted, the original rear sight and front sight are present, as is the original bayonet lug, the original full-length ramrod and both sling swivels. Even the original screw protecting “doughnuts” are present at the ends of the tension screws for the two Palmer pattern clamping bands. All of the brass furniture from the buttplate to the nose cap has a smooth patina that matches the balance of the gun well. The stock is in about VERY GOOD condition and is made from an attractive and nicely figured piece of walnut. The stock is solid, full-length, and complete and free of any repairs, breaks, with a few hair-line cracks near the butt-plate. The stock retains very good line and edges and does not appear to have been sanded. Overall, this is a very attractive, 100% complete and correct example of a commercial or “Volunteer” version of the Pattern 1855 Royal Engineer’s Carbine. Shipping & Insurance included. $2100.00
*****************************************************************************************************************************
F433. COLT MODEL 1851 NAVY REVOLVER – 1861: This is a Colt Model 1851 Navy Revolver; Serial Number 104103; (Manufacture Year – 1861. The serial number matches on all parts to include the wedge, loading lever and cylinder. The grips is original as are all screws. The Colt maker mark on the top of the barrel is very strong, but there is some pitting, and the cylinder scene is visible, but also has some pitting. Most likely it is from gun power residue. The action properly cycles; holds in both half and full cock positions; and the rifling is strong. The gun is very tight. Shipping & Insurance included. $2300.00
*****************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F437. CONFEDERATE – CAPTURED & REPAIRED COLT SPECIAL RIFLE: This is a highly desirable Union Colt Special Rifle, which was Confederate captured and went through the C & R system located around Richmond VA and inspected by Lous Zimmer and marked with the letter "Z" on the underside, forward of the trigger tang. During the C & R process, vice-clamps were often used and upon close examination you will see evidence of clamp use in the wood forward of the lock plate and on the face plate front screw. The lock is dated 1864 and part of the Cott marks was buffed off during the C&R repairs. The gun is full length; properly functions, and has the original sites and sling swivels. Shipping & Insurance is free. $2500.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
F444. SPENCER CARBINE – CONFEDERATE CAPTURED CLEANED and REPAIRED “&” MARK: This is a Spencer carbine, serial number #22061 with a Confederate Cleaned and Repaired “&” inspection about 1-inch below the trigger guard. The nearest identified Spencer carbine is serial number 21982, which was issued to a soldier in Co. D 5th New York Cavalry. In all likelihood, this gun was carried by a New York soldier and lost on a battlefield in Virginia; recovered and sent to Richmond to be cleaned, repaired and reissued. When reissued, it would look new and came with a limited supply of captured ammunition.
This gun saw heavy use after it was refurbished. The stock has a deep brown patina with lots of dings and bumps, and has a crack which is on both sides of the stock down its center. However, the stock is solid with no movement and is tight. All the metal has a deep brown patina; the action is tight and holds both half and full cock, and the loading tub is present, but missing the inner spring. The Confederate soldier who had this gun use it hard, and maybe when the ammunition ran out, it became a club. Recently, one in fine condition sold for $3500,00, but since this is a heavily use example, it is available for less. Here is a chance to own a Confederate captured, cleaned, and repaired Spencer Carbine that saw the elephant, and a lower price. Shipping & Insurance included. $1900.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
******************************************************************************************************************************
CLICK THE ABOVE ICON TO READ THE COMPLETE HISTORY FOLDER
"Z"
F477. JOSLYN CARBINE - UNIT ISSUED AND IDENTIFIED & CONFEDERATE RECOVERED & REISSUED: This Joslyn carbine, serial number 993, was used by 2 different soldiers from Company H, 19th New York Cavalry, known as the 1st New York Dragoons. It was first issued to Corporal George Dean, then to Private George Underhill after Dean was wounded at Manassas Junction and assigned to the Ambulance Corps. Underhill would be involved in several engagements and later lose the gun during the fighting at Trevillian Station Virginia on 12 June,1864 when he sustained a gunshot wound of the left leg. The carbine was later Confederate recovered off the battlefield; sent back to Richmond and went through the “C&R” Clean & Repair system at the Richmond Arsenal/Artillery Work shop; inspected by Lous Zimmer and marked with the letter "Z" on the underside, forward of the trigger tang. The gun is fully functional with expected bumps and dings, and is in great shape considering it saw heavy use and action. A 144 page binder on the unit's history and the soldiers is included. Shipping & Insurance included. $6500.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F481. IMPORTED AUSTRIAN M-1854 LORENZ RILE: This is an Austrian M-1854 Lorenz Rifle Musket, as imported by the Confederacy during the course of the American Civil War. The Lorenz was the third most used infantry arm on both sides during the war, and somewhere between with the US importing approximately 250,000 of the guns during the war and the Confederates importing at least 100,000, and quite possibly more. The Confederacy was always thought to have purchased most of their Lorenz’s after Caleb Huse visited Vienna as the Confederate Ordnance Department purchasing agent 1863, however more recent research indicates that Huse purchased his first Lorenz rifle muskets through S. Isaac, Campbell & Co of London in 1862. It appears that many of the guns that were purchased by the Confederacy were in their original 13.9mm caliber (about .547), while many of the US purchased guns were re-bored to more closely approximate the standard US caliber of .58. The importance of the .54 caliber Austrian M-1854 Lorenz to the Confederacy might best be illustrated by an invoice from the famous English ammunition manufacturer Eley Brothers. The invoice is contained within the McRae Papers, and is dated July 18, 1863 “ some two weeks after the Battle of Gettysburg and the fall of Vicksburg, MS. The invoice is for 700,000 paper cartridges. The order included “600,000 Austrian Rifle Cartridges “ Marked A” and “100,000 Ball & Buck Short Musket Cartridges “ Marked M”. While the caliber of the Austrian cartridges is not specified, it seems clear that the order would be for .54-caliber ammunition, as the order contains no request for any .58 ammunition.
The rifle is in good working order and properly functions and has all original barrel bands and sling swivels. The gun saw heavy action and the rifling is shoot out. The lock is marked 860 for 1860 and the hammer screw has a unique field replacement. The wood is complete with no crakes or breaks with a large cheek rest on one side and carved letters on the other, and the original fixed tombstone rear site. Shipping & Insurance is free. $1750.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
F500. CONFEDERATE CAPTURED & CARRIED STAR CARBINE: About 20,000 Starr percussion Carbines in .54 Caliber were bought by the Union during the Civil War, most of which were issued to Western troops. This weapon has a dropping breach, similar in action to the Sharps, and was rated as better in government tests, and was produced by the Starr Arms Company located in Yonkers, NY. They had a brass buttplate and barrel band, and the iron parts were blued with case – hardened lock and frame. They were all serial numbered with the lock marked STARR ARMS CO/ YONKERS. N.Y. The barrel is stamped STARR ARMS CO YONKERS, N.Y and the breech is stamped STARR’S PATENT / SEPT. 14th 1858. This is serial number 8292, which is close in range to the guns issued to the 3rd Arkansas cavalry (USA). However, there are several carvings on the gun that indicated it was Confederate captured and carried by a Southern cavalry soldier. The walnut stock has normal nicks and scratches seen with a carried gun and a brown patina, but there are several carvings commonly associated with the Confederacy: three Confederate flags carved into the left cheek stock, one with 6 stars, and there is an additional Confederate flag carved forward of the trigger. Additionally, there are three different sets of initials: “J S” “I M” and “B B B.” The initials "J S" are faint, with the S carved in reverse, and an unknown carving before these initials. On the opposite side are the initials “I M” and “B B B.” The Arkansas 1st Cavalry (Confederate) did have soldiers with these initials, but a positive identification is extremely difficult without more information. The bore is bright with strong rifling, and the action is mechanically perfect. Shipping & Insurance included. $2200.00
*****************************************************************************************************************************
CLICK THE ABOVE ICON TO READ THE COMPLETE HISTORY
F505. MISSOURI IDENTIFIED - 1853 ENFIELD RIFLE - SERIAL NUMBER BUTT PLATE - JS ANCHOR: This Pattern 1853 Enfield Rifle is identified to William D. Maupin: Missouri State Guard & Missouri 1st Cavalry. Both units fought as dismounted infantry during the war. This is a serial numbered rifle and was in the first lot of 10,000 purchased by the Confederate Government: Serial Number 4868. It is also “S” marked forward of the butt plate and JS-Anchor to the rear of the trigger guard tang. The lock is CROWN and TOWER 1862 marked and properly functions, but the rear sight blade is missing. The bore is dark and nearly shot-out, but you can see faint rifling, and the ram-rod is period with patina that matchedthe rifle.
“W. D. Maupin” is carved on the front side of the butt stock. Some lettered are more pronounced than others, but are present. A search of the Civil War data base and National Civil War records found only one Confederate soldier with this name: Willian D. Maupin. He most likely was issued this rifle when he enlisted in the Missouri State Guard and retained it when it joined the Missouri 1st Cavalry. Both units fought dismounted for most of the war.
He may ormay not have carried it after he assumed command when promoted to Lieutenant Colonel, but we know that whatever he carried at the Battle of Corinth he discarded it to pick up the regimental flag shortly before he was killed.
William D. Maupin began his Confederate service in the Missouri State Guard (MSG) as a Private and Sergeant: date of enlistment unknown. The Missouri State Guard was a military force established by the Missouri General Assembly on May 11, 1861. While not a formation of the Confederate States Army, the Missouri State Guard fought alongside Confederate troops and, at various times, served under Confederate officers. Maupin joined the 1st Missouri Cavalry on December 7, 1861, so it can be surmised he was into the Missouri State Guard between May 11, 1861 & December 6, 1861 and saw action in some of the encounters fought by the Guard.
During his time of service, the Missouri State Guard fought in the following engagements: First Battle of Boonville, June 17, 1861; Battle of Cole Camp, June 19, 1861; Battle of Carthage, July 5, 1861; Battle of Dug Springs, August 2, 1861; Battle of Athens, August 5, 1861; Battle of Wilson's Creek, August 10, 1861; Battle of Dry Wood Creek, September 2, 1861; Action at Blue Mills Landing, September 17, 1861; First Battle of Lexington, September 13 to 20, 1861; Battle of Fredericktown, October 21, 1861; First Battle of Springfield, October 25, 1861.
On December 7, 1861 at the age of 25, William D. Maupin enlisted as a Private into the Missouri 1st Cavalry, and was elected Captain on December 13, 1861; Company A, Missouri 1st Cavalry. He would serve as a captain for 6 months until June 1862 when he was promoted to Lieutenant Colonel and took command: June 29, 1862. His muster sheets document him as a Lt. Col at Priceville, MS, June 15, 1862 and he was engaged at Carthage, Oak Hill, Dry Wood, Lexington, Sugar Creek, Bentonville, Elkhorn, Farmington, Iuka, and Corinth where he was killed on field of battle October 5, 1862. Colonel William D. Maupin (1st Missouri Cavalry, fighting as infantry) fell while bearing the flag of his command after two color bearers had fallen. Shipping & Insurance included. $6700.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
F511. IVORY GRIP COLT MODEL 1860 ARMY REVOLVER – RECONSTRUCTION PERIOD: This ivory grip Colt Model 1860 Army Revolver is serial number 170662, which places it in the year 1868 right at the beginning of Reconstruction; the period after the Civil War when the former Confederacy was reintegrated into the United States.
The Military Reconstruction Act of 1867 divided the former Confederacy into five military districts, and the U.S. Army played a key role by enforced laws, protected freed slaves, protected polling sites and registered voters, and enforced laws that protected the voting rights and safety of African Americans.
This revolver is all original with matching serial number 170662 on all parts to include the cylinder, wedge and steal back strap. The grips show the expected wear, shrinkage, and stress fractures common to period ivory, but no breaks and are tight. The frame and cylinder have an even gray patina; the action is tight and properly functions, the bore has strong rifling; there remains a good amount of cylinder scene; and the brass trigger guard has traces of original silver wash. Shipping & Insurance included. $3600.00
*****************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F516. SHARPS CARBINE - CONFEDERATE CAPTURED, CLEANED & REPAIRED: This Sharps Carbine went through the Confederate C&R (clean, repair) process and has the inspection mark “Z” on the underside to the rear of the trigger tang. This mark is associated with Captain Louis Zimmer, who was involved with Confederate clean and repair operations at Richmond. The mark is faint indicating the gun was reissued to a Confederate soldier and most likely saw some action. The original serial number is 97222. The gun is in great shape with nice dark walnut stock and forearm and an even patina on all metal parts, and the original patch box. The Confederate C&R guns are very collectable, as well as affordable, compared to a Richmond rifle or carbine. Free Shipping & Insurance. $3600.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F518. AUSTRAIN M1851 CARBINE – TYPE-II: The Austrian M1851 Carbine have long been considered early Civil War Federal purchased, but new information indicates they saw Confederate service as well. Originally designed with the Austrian console (pill lock) ignition system, they were altered to percussion in the late 1850’s. It measures 30” overall with a 14.5” barrel and a .71 caliber bore with distinctive 12-grove rifling. The type-II variant has a Belgian alteration with the bolster on top of the barrel, and no ramrod. The ramrod was carried separately on the soldier’s belt. This gun is in near-mint condition with crisp edges, bright metal, and matching serial numbers. The action is tight and properly functions. This is the finest example I have ever seen! Shipping & Insurance included. $1800.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
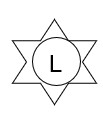

F519. CONFEDERATE - LOUISIANA - PURCHASED 1853 ENFIELD RIFLE: This Confederate Enfield was purchased by the State of Louisiana and is extremely rare. They were double stamped with a hexagram (six-point star) surrounding the block letter “L” in the center, which would be found on the underside of the stock to the rear of the trigger guard. The rifle is 100% original; never clear; has all barrel bands; original ramrod, Lower sling swivel, but missing the top swivel. The lock is marked CROWN 1861 over TOWER and properly functions and the hammer screw is numbered 92. The rear site is complete and works. This is a recently discovered example to be added to the hand full of known Louisiana Enfields. Shipping & Insurance included. $14,000.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
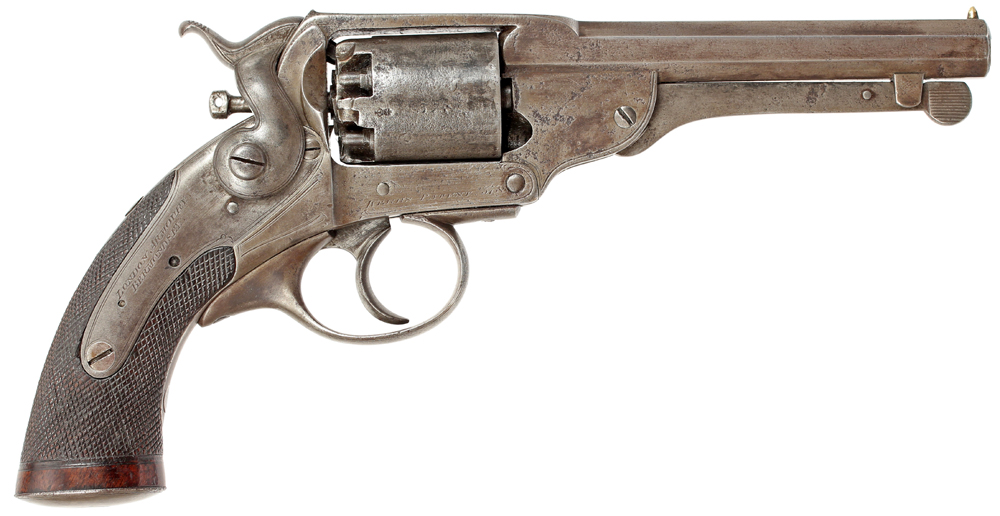
F520. COLT MODEL 1851 NAVY REVOLVER (.36 CALIBER WITH NAVAL ENGAGEMENT ON CYLINDER, OCTAGONAL BARREL): This is a Colt Model 1851 Navy Revolver with matching serial number 140585, except for the period replaced wedge: production year 1863. This serial number falls between those issued to the 8th Michigan cavalry.
140576 51N 64 CO K 8TH MICH VOL CAV
140602 51N 65 CO B 8TH MICH VOL CAV
The gun has a brown-gray patina, all original screws; properly function and holds in both half & full cock positions; all original nipples, full naval scene above the cylinder serial number; original grip with a silver inlay of an upward pointing heart. This heart may represent the 24th Army Corp. Shipping & Insurance is included. $2500.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F521. COLT 1851 NAVY REVOLVER (.36 CALIBER WITH NAVAL ENGAGEMENT ON CYLINDER, OCTAGONAL BARREL: This is a Colt Model 1851 Navy Revolver with matching serial number 175959: production year 1864. All parts to include the cylinder and wedge have matching numbers. This gun saw use and has an even gray patina. The action is tight and hold both half & full cock positions and properly functions. It has the original grip; screws and nipples but little cylinder scene, and there are two areas on the grip that have lead applied. Shipping & Insurance included. $1995.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F522. COLT 1851 NAVY REVOLVER .36 CALIBER WITH NAVAL ENGAGEMENT ON CYLINDER & OCTAGONAL BARREL: This is a Colt Model 1851 Navy Revolver with matching serial number 127682-2: production year 1862. The gun has lots of original blue as does the wedge, which is original to the gun, but was factory struck several times caused the last digit to look like an 8. The gun has much original blue on the upper barrel receiver, and a pleasing light brown patina on the lower receiver and cylinder with some traces of blue. All screws are original, and the cylinder retains much of the original scene. The grip is original and has 3 (///) hash marks on the bottom wood. The backstrap has traces of gold wash, and what appears to be the remnant of a presentation or identification, and a partial date 23, 1863 on the underside brass. These marks are faint and best visible with magnification and are difficult to photograph. Obviously, the gun was carried and these marks are faint, but Colt research center might have more information on this gun and it may be worth the extra $350.00 they charge to see what they know. Shipping & Insurance is included. $3800.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F523. COLT MODEL 1860 ARMY REVOLVER (.44 CALIBER WITH NAVAL ENGAGEMENT SCENE ON CYLINDER) All MATCHING NUMBERS: This is a Colt Model 1860 Army revolver, .44 caliber with naval engagement scene on cylinder and all matching numbers to include the wedge and cylinder. It has an 1863 serial number 134691, and faint cartouche marks on both grips. On SEP 09, 1863, the New York Arsenal Governor's Island, NY received 1000 Colt 1860 Army revolvers and this gun was within the range of this shipment. The gun has a gray-brown patina; has all original screws; properly functions and holds both in half & full cock position; all original nipples; and traces of original cylinder scene. Shipping & Insurance is included. $1995.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F524. HARTFORD COLT M1851 NAVY REVOLVER- 1861 PRODUCTION: This is a Hartford Colt – Model 1851 Navy revolver: production year 1861. Most likely the gun was made at the end of 1861 because it was sold to the United States Government on January 11, 1861 per the Colt historical records. The gun is compete with all matching serial number 99667 to include the cylinder and wedge. The grips and all screws are original; the action properly functions and holds both half & full cock; the nipples are all original, and the gun has a gray patina. Included is the Office of the Colt Historian letter document the gun beind sold in a lot of 100 to the United States Government and shipped to Colt's Patent Fire-Arms Mfg. Company, New York Office. Shipping & INsurance included. $2800.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F525. COLT MODEL 1861 NAVY REVOLVER: This revolver, which I took in trade, was discovered by Brian Ankins fresh out of the Texas Hill Country. Here is his description: “This Colt Model 1861 Navy Revolver has all matching serial numbers, included the wedge. The condition is solid but has been cleaned at some point. No doubt saw some action during the War of Northern Aggression, but action works and displays good.” The screw above the wedge is replaced. Shipping and Insurance is included $1650.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F526. CONFEDERATE CONVERSION “COMMON RIFLE” - ROBINSON CONVERSION: This is a Confederate Conversion “Common Rifle” Robinson Conversion. The bolster and hammers scream Southern with the brass brazing and its crude appearance. The is in excellent condition with its original double cartouche and the barrel and lock are dated 1841. The action properly function, though a little soft. The blade rear site is present and well has the cap-box cover and all original screws. The “Common Rifle” is a great addition to a collection, especially one that is a Confederate conversion. There are as Southern as a Richmond or Fayetteville rifle or Enfield, just not as expensive. Shipping & Insurance included. $2600.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F529. CONFEDERATE - SHARPS CARBINE – CAPTURED CLEANED and REPAIRED “L” MARK: The Sharps carbine was a widely used, highly reliable .52-caliber single-shot, breech-loading weapon, primarily utilized by Union cavalry during the American Civil War.
This gun was Confederate captured and sent to Richmond to be Cleaned, Repaired, Inspected and Reissued. The gun is in amazing condition with a strong bore, great patina on the metal, fully functional and Inspection marked with the letter “L” which was double-struck (double-tapped) when stamped. Its serial number is C7819.
The uncommon letter stamp “L” indicates cleaning and repair has been performed at a Confederate arsenal or depot and the mark denotes the final inspector of the C&R process. The “L” stamp likely corresponds to inspector Lieutenant George Lemmon, who was assigned to the Richmond Arsenal/Artillery Workshop in January – February 1865. To date, there is a known examples of Remington Army revolver with the inspection “L” mark and one other Sharps Carbine, both in a private collection in Fredericksburg Virginia.
Since the publication of the book on the C&R process, several other inspection letters have been identified: A,T,F,Q,Z were the original marks and &,D,B,L,X,S have been added. To date, I have seen all but the letter S, and the font size is the same. Research is still ongoing and new information is coming to light as Capt, Steven W, Knott, USN (ret) continues his research on this topic. Shipping & Insurance is included. $4700.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F530. CIVIL WAR ERA REMINGTON OLD MODEL NAVY .36 CAL PERCUSSION REVOLVER: This is a Remington Old Model Navy Revolver. It is .36 caliber with a 7 3/8-inch octagon barrel and has a worn original blue finish, about 40-50%. The grips are original, but have been sanded. The action is tight and properly functions, but the bore does have some pitting and other wear from age. It has a two-line patent stamp on the top of the barrel with the date SEPT 14 1858 and a Navy anchor proof mark. The serial number 27711 under the barrel is very difficult to read, but is strong under the grip. There is also a proof mark "M" on the left side of the brass trigger guard. The cylinder may be a period New Model cylinder due to the safety notches which was common during the period. Shipping & Insurance is free. $1100.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F531. DEANS ADAMS MODEL 1851 REVOLVER BY TRANTER – RETAILED BY E & W BOND, LEADENHALL St. LONDON: This is a very attractive example of an English Deans Adams Model 1851 self-cocking (double action) revolver. These fine quality, solid frame revolvers were as important to the history and development of the revolving handgun as were the developments and designs of Samuel Colt. Robert Adams received his patent for a solid frame, one-piece revolver design in 1851. The patent covered his novel concept for a very strong revolver, where the frame and barrel were machined from a single steel forging. Unlike practically every other revolver design of the period, where the barrel and frame were separate components that were joined by wedges, screws, or some other mechanical system. Adams additionally patented a self-cocking lock work, which today would be referred to as “double action only.” This mechanism cocked the hammer, rotated the cylinder, and released the hammer, all as the result of a single pull of the trigger. While this allowed for rapid fire, the long, heavy trigger pull inhibited accurate shooting. These designs were incorporated into Adams Model 1851 self-cocking revolver. The major drawbacks to Adams’ Model 1851 design were the heavy double action only trigger and the lack of an integral loading lever, requiring lading tools to be transported with the gun if it needed to be reloaded while being carried. Many of the Adams revolvers encountered today are double“serial numbered,” with one “serial number” being the number that tracked the royalty payments due to Adams on his solid frame patent. These numbers are typically marked with a suffix letter that indicates the manufacturer using the patent (for example “T” for Tranter, “B” for Brazier and “X” for Hollis & Sons).
The Adams revolvers, in their .54-Bore configuration (about .442 caliber), were one of the best combat revolvers of the mid-19th century and as such a number of them were imported for use during the American Civil War. However, the lack of records makes it is difficult to ascertain exactly how many Adams’ patent revolvers were imported for use during the American Civil War. At least 1,075 were purchased directly by the US government. It is known that some military outfitters like Schuyler, Hartley & Graham purchased quantities of these revolvers for private sale to officers and those volunteer groups who looked to their state and local government (rather than the US government) to purchase arms. Some of the Schuyler, Hartley & Graham guns (about 300) are reported to have been purchased by the state of Alabama prior to the start of the war. Virginia and Georgia are reported to have made pre-war purchases of these revolvers as well.
Confederate speculators and individual states did purchase these fine English revolvers in some quantity. In fact, many Adams revolvers, manufactured by the London Armoury Company, are believed to have been in the L.A.C. inventories at the outbreak of the war. It seems quite probable that when Major Anderson and Commander Bulloch initiated their relationship with Archibald Hamilton (of Sinclair, Hamilton & Co, and the managing director of the London Armoury Company) that they arranged for a substantial number of these revolvers to be delivered to various Confederate states and to the Confederate Navy.
Civil War regiments that are known to have carried or been issued Adams’ patent revolvers include the 8th PA and 2nd MI cavalry on the US side and the 1st, 5th & 18th VA and 5th GA cavalry on the CS side.
This gun is in great condition with much original blue finish remaining; properly function; has the proper English Proof marks on the barrel and cylinder, and strong rifling. The serial number is No. 2680 T, which means the gun was manufacturer by Tranter, and retailed by E & W Bond, Leadenhall St. London. Shipping & Insurance included. $2995.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F532. 1863 MODEL STARR SINGLE ACTION ARMY REVOLVER: The Starr Arms Model 1863 Percussion “Army” Revolver was designed as a simplified and more robust version of their earlier Starr Model 1858 Double Action Revolver. The simplified action was also intended to be less expensive to produce and thus more cost effective, for the US Government to purchase. Like the earlier M1858 Double Action Army, the gun was a six shot, .44 caliber percussion revolver. However, the M1863 utilized a single action lock work, instead of the delicate and complicated double action lock of the M1858. The M1863 also had a longer barrel, measuring 8” in length. This was an increase of 2” over the earlier M1858. The production of the M1863 started at about serial number 23,000, continuing from the end of the production run of the earlier M1858 Double Action revolver. Some 32,000 of the “improved Army” revolvers were produced by the Starr Arms Company between the end of 1863 and the end of 1865.
In September of 1863, Starr received a contract to deliver 25,000 of their Improved Army. The contract specified that 1,000 guns were to be delivered during the month of October (1863), with additional deliveries of 2,000 guns per month over the next twelve months until the contract was fulfilled. Starr delivered the first 1,000 of the Single Action M1863 revolvers in December of 1863 and a total of 24,002 over the twelve months of 1864. During the American Civil War, the M1863 Starr was issued to several US cavalry regiments, including the 1st Colorado Cavalry, the 6th & 7th Michigan Cavalry, and the 11th New York Cavalry, just to name a few.
This example of the Starr Model 1863 Single Action Army revolver remains in about Good+ condition with an even brown patina. The right side of the gun is marked STARR’S PATENT JAN 15 1856 and the left side is marked STARR ARMS Co NEW. YORK. There are a variety US government sub-inspector marks crisply stamped on the frame, barrel, cylinder, and trigger guard, which include the capital letters L, B, C and Y. The matching serial number of 29068 is present on the center of the lower front of the frame below the loading level recess, in the hammer cut out in theupper rear of the frame and on the cylinder.
This serial number places this gun smack in the middle of two known guns issued to the 7th Michigan Cavalry.
27322 07 64CO K 7TH MICH VOL CAV
29217 07 64CO K 7TH MICH VOL CAV
The gun has an even brown patina; properly functions; has strong rifling and the original grips. The grips are worn with dings and bumps and there is a very faint partial outline of top of the cartouche mark. The right grip appears to have three hash-marks. Shipping and Insurance is included. $1975.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F533. HARTFORD CT. COLT M-1851 NAVY - NAVY REVOLVER: This is a VERY GOOD++ to NEAR FINE example of a US Navy inspected Colt M-1851 Navy revolver. The number of Colt’s .36 caliber M-1851 “Navy” revolvers purchased by the US Navy was rather limited. Colt sold the Navy 50 M-1851 revolvers in June of 1856 and an additional 50 revolvers in May of 1857. In September of that year, the Navy placed a large order for M-1851 revolvers. They purchased 2,000 (less the ones that had been previously ordered), which were delivered starting in November of 1857. These guns appear in the 55500 to 62000 serial number range. The first 615 were delivered for inspection at the Norfolk Naval Yard on November 9, 1857. The next batch of 667 were delivered to the Boston Naval Yard on December 6, and rest of the guns were delivered to the New York Navy Yard later that same month. The Navy placed a second order for an additional 600 M-1851’s in August of 1859. These guns were in the 89000 to 91000 serial number range, with half of the guns delivered to the New York Naval Yard and the other half delivered to the Boston Naval Yard. By 1860, Colt M-1851 revolvers were listed in the small arms inventories of nearly 30 US Naval vessels, including the USS Caledonia, USS Colorado, USS Congress, USS Crusader, USS Cumberland, USS Decatur, USS Fennimore Cooper, USS Fulton, USS Independence, USS John Adams, USS Lancaster, USS Merrimack, USS Mississippi, USS Pawnee, USS Plymouth, USS Porpoise, USS Powhatan, USS Portsmouth, USS Roanoke, USS Sabine, USS Saranac, USS Saratoga, USS St. Mary’s, USS Susquehanna, USS Vincennes, USS Wabash, USS Water Witch & USS Westernport.
This a Hartford CT Colt M-1851 Navy-Navy revolver is part of the second order for 600 guns and was delivered to the New York Navy Yard. The revolver has the matching serial number 89823 on all the major parts, with the loading lever, the barrel wedge and the cylinder arbor having the matching number 9823. The inside rear channel of the walnut grips is numbered in period ink, and the ink is worn and faded, but appears to read 9823 as well. The revolver has an iron backstrap and trigger guard. The lower front portion of the left side of the frame is marked in three lines: COLT’s / PATENT / U. S. The octagon barrel is marked with the single line New York barrel address that reads: “ ADDRESS SAML COLT HARTFORD CT”. The bottom of the iron grip strap is clearly marked: U S N and the bottom of the wooden grips are marked: I / G W R, indicating inspection by Lt. George W. Rodgers, Ordnance Inspector at the New York Navy Yard.
The gun remains very crisp throughout, with sharps edges on the octagonbarrel and very clear markings in the metal and the wood. The balance of the finish has worn and faded, blending with a smooth charcoal gray patina. The metal surfaces are mostly smooth, with very small patches of light pinpricking scattered over the entire gun. The cylinder retains about 90%+ of the roll engraved Mexican War naval battle scene. All the cones (nipples) in the cylinder are original, but do show use, with pinpricking and expected surface oxidation, and all safety pins on the rear face of the cylinder are in very nice condition as well. There is also some pinpricking on the face of the cylinder from firing and use.
The gun appears to retain all original screws, which are in very nicecondition and show expected wear and the action is tight, but must be cocked with a little force to stay in the full cocked position. The bore is pitted with good rifling and rates about GOOD.
The one-piece, oil finished, black walnut grip is in about EXCELLENT condition, and is free of any breaks, cracks, or repairs. The grip does show some handling marks from use and some minor dings and tiny surface mars, but even the leading edges remain in very crisp condition. The inspection marks in the bottom of the grip are in wonderful condition and are much better than are normally encountered on Colt “Navy-Navies."
Overall, this is a lovely, 100% complete and correct, allmatching Colt M-1851 Navy-Navy. These are very scarce guns, with only 2,600 of the guns being procured via contract with the Navy. At least 1,000 of the Navy purchased Colts were subsequently altered from percussion to .38 Center Fire by Colt, for the Navy, in 1873. This makes the original percussion “Navy-Navies’ even rarer. Considering that Colt produced over 215,000 of the M-1851 revolvers in Hartford, these USN marked M-1851 Navy revolvers represent only 1% of the total production. This gun has a wonderful look and has not been messed with in any way, and it would be hard to imagine finding one with crisper and clearer inspector markings. Shipping & Insurance included. $2995.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F534. REMINGTON NEW MODEL ARMY REVOLVER – 5TH ILLINOIS VOLUNTEER CAVALRY SERIAL NUMBER RANGE: This Remington New Model Army Revolver is serial number 28996, which is one digit from a known 5th Illinois issued Remington revolver: 28995 A 65CO E 5TH ILL VOL CAV (ISSUED). As such, there is a high probability this gun also went to this unit.
The 5th Illinois Volunteer Cavalry Regiment (1861–1865)was a prominent Union unit in the American Civil War, organized at Camp Butler, Illinois, and known for service in the Western Theater, notably the Vicksburg Campaign. Key Campaigns & Actions: The regiment participated in the advance on Corinth (1862), the Siege of Vicksburg (1863), and operations near Canton, Mississippi. Major Battles: Battle of Corinth (Oct 1862), actions around Snyder's Bluff (June 1863), and various skirmishes in Missouri, Arkansas, and Mississippi.
The revolver is in Good++ to Fine condition with much original blue finish. The action is tight and properly cycles and holds both half & full cock positions. The grips are original with a faint cartouche on the right side, and a crack that was period repaired. Normally the barrel is 8 inches long, but this is 7 1/4 long with vice-clamp marks indicating the barrel was removed and period shortened, most likely from damage in the field, and an added brass front site. The Remington New Model mark on the barrel top is very strong. Shipping & Insurance included. $2100.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F535. REMINGTON-BEALS ARMY (.44 CALIBER) REVOLVER – 1ST IOWA VOLUNTEER CAVALRY RANGE: The Remington-Beals Army (.44 caliber) revolver, produced from roughly 1861–1862, is a scarce early model with an estimated production of only about 1,900 units. Serial numbers for these, often featuring an 8-inch barrel and lacking a loading lever latch, are generally low, with examples identified as low as 1550. This gun is rarer with a serial number of 971, which is within the range of guns issued to the 1st Iowa Vol. Cavalry.
The 1st Iowa Volunteer Cavalry was one of the earliest Union cavalry regiments to enter the field during the Civil War, and they were initially equipped with Remington-Beals Army (.44 caliber) and Navy (.36 caliber) revolvers. The records list all Iowa issued Beals revolvers as NB.
937 NB 110162CO F 1ST IOWA VOL CAV (ISSUED)
980 NB 110162CO F 1ST IOWA VOL CAV (ISSUED)
The top barrel flat is marked “BEALS' PATENT. SEPT. 14. 1858. / MANUFACTURED BY REMINGTONS' ILION. N.Y.” The gun has an even gray patina; is all original; properly function; and has original grips, both which have cartouche marks: Left grip N W ( Nathaniel Whitine) Right grip W A T ( William A Thornton. Martially marked Beals are extremely rare to find, especially one within the range of guns issued to the 1st Iowa Cavalry. Shipping & Insurance included. $2795.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
F536. REMINGTON NEW MODEL ARMY REVOLVER – 19TH NEW YORK VOLUNTEER CAVALRY SERIAL NUMBER RANGE: This Remington New Model Army Revolver is serial number 55123, which is one digit from a known 19th New York Vol. Cavalry issued Remington revolver: 55124 A 10 64CO I 19TH NY VOL CAV. As such, there is a high probability this gun also went to this unit.
The 19th New York Volunteer Cavalry Regiment, also known as the 1st New York Dragoons, was a prominent Union cavalry unit during the American Civil War. The regiment was organized at Portage, New York, and officially mustered into service on September 2, 1862. The regiment earned a high reputation for discipline and was involved in approximately 65 battles and skirmishes.
The revolver is in Good+++ condition with a gray finish, light traces of original finish, and sharp edges. The action is tight and properly cycles and holds both half & full cock positions. The grips are original with a barely visible cartouche on the right side. The soldier who carried the revolver carved out the grip for a lanyard, and scratch his initials on the bottom. The barrel has strong rifling and the Remington New Model mark on the barrel top is very strong. Shipping & Insurance included. $1700.00
******************************************************************************************************************************
****************************************************************
Remittance by Mail
Send to:
Arizona Swords
530 E. McDowell Road, Suite 107-160
Phoenix, AZ 85004
****************************************************************
Contact Number: (602) 245-4721
© 2004 Arizona Swords azswords.com. All rights reserved in all media.